[Weekly News] CRISPR-Cas9 Screening Shines: A More Sensitive and Specific Method to Identify Fetal Hemoglobin Inducers

The CRISPR/Cas system, a revolutionary tool in modern biological science, impacts fields ranging from medicine and agriculture to environmental conservation. Every week, new research developments and application cases related to CRISPR continue to emerge, bringing profound changes to our lives. Below is a brief overview of the latest CRISPR-related research and industry news from the past week:
I. Research Update
a) CRISPR Screening
1. Article Title: A cellular reporter system to evaluate endogenous fetal hemoglobin induction and screen for therapeutic compounds
Journal: HemaSphere (IF: 12.1)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/hem3.139
Recently, Dutch researchers published their latest findings—a novel CRISPR-Cas9-mediated reporter cell line for evaluating endogenous fetal hemoglobin (HbF) induction and screening therapeutic compounds. This innovative method aims to identify HbF inducers by utilizing a reporter cell line, which is the first to successfully label the endogenous fetal globin genes, HBG1 or HBG2. The new assay is based on HUDEP2 cells, which closely resemble adult erythroid progenitors and do not upregulate HbF under stress, unlike primary erythroid cells.
The study used CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knock-in to integrate a bioluminescent tag into the HBG1 gene and successfully demonstrated that the resulting reporter cell line reflects the characteristics of HUDEP2 cells, enabling highly sensitive and specific reporting of fetal hemoglobin induction.
This new tool offers a more specific and sensitive approach to identifying potential HbF therapeutic inducers, marking a significant improvement over previous systems.
2. Article Title: Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens identify DNMT1 as a druggable dependency in sonic hedgehog medulloblastoma
Journal: Acta Neuropathologica Communications (IF: 6.2)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-024-01831-x
Smoothened (SMO) inhibitors have shown promise in treating medulloblastoma, but resistance to these treatments remains a persistent challenge. To address this issue, German researchers conducted a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen to explore genetic dependencies and drug-related genetic interactions in the Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) subgroup of medulloblastoma (SHH-MB), aiming to identify alternative therapeutic targets.
The study identified DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) as a crucial epigenetic target. In SHH-MB models, inhibiting DNMT1 alone or in combination with SMO inhibitors significantly reduced tumor growth and extended survival.
This research provides strong evidence for the broad applicability of CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens in drug development.
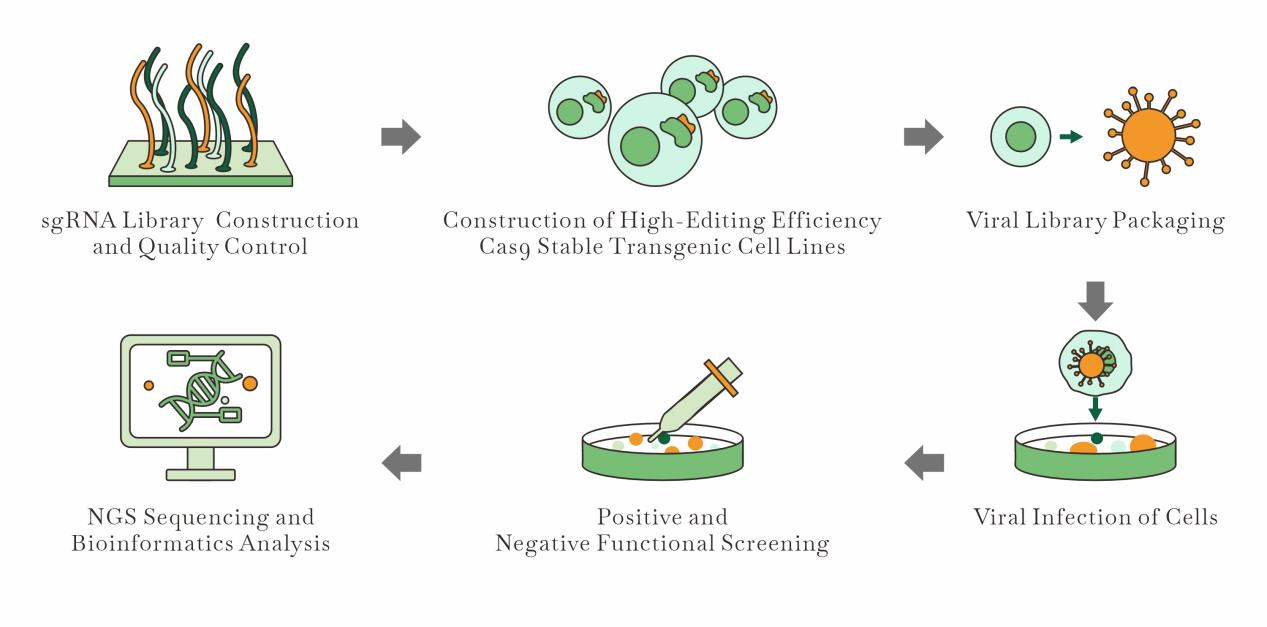
Crispr Screening Workflow | EDITGENE
b) CRISPR Detection
1. Article Title: SATCAS: A CRISPR/Cas13a-based simultaneous amplification and testing platform for one-pot RNA detection and SNPs distinguish in clinical diagnosis
Journal: Biosensors and Bioelectronics (IF: 10.7)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2024.116636
The demand for RNA detection technologies in clinical diagnostics, particularly for pathogen-related infectious diseases, is increasing, requiring more sensitive and rapid methods. The CRISPR/Cas13a system, known for its post-transcriptional cleavage activity, shows significant potential in molecular diagnostics. However, most existing Cas13a-based detection methods require a transcription amplification step, which can lead to contamination due to multi-step open operations.
To address this, researchers from Peking University and Fudan University have developed a highly sensitive (single-copy level, approximately aM range) and rapid (within 40 minutes) isothermal one-pot RNA detection platform called SATCAS.
This platform effectively distinguishes active bacteria (0%-100%) and excels in single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) identification, particularly in detecting 0.5% drug-resistant mutations. By testing biological samples from 68 HBV, 23 EBV, and 48 SARS-CoV-2 patients, SATCAS achieved 100% sensitivity, 92.86% specificity, and 97.06% accuracy. This platform is suitable for detecting cultivable pathogens and diagnosing viral infections in clinical settings.
2. Article Title: Harnessing the power of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) based microfluidics for next-generation molecular diagnostics
Journal: Molecular Biology Reports
Link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09840-8
Despite CRISPR's high precision, its application is still limited by high costs, technical demands, and difficulties in quantification. Microfluidics, with its capabilities for miniaturization and process automation, addresses these challenges by making detection more sensitive, portable, and accessible.
Recently, researchers in India published a review summarizing the integration of CRISPR systems with microfluidic platforms for diagnostic applications. The review discusses various CRISPR-Cas systems and their applications in detecting DNA and RNA biomarkers, offering valuable insights for advancing CRISPR-based molecular diagnostics.
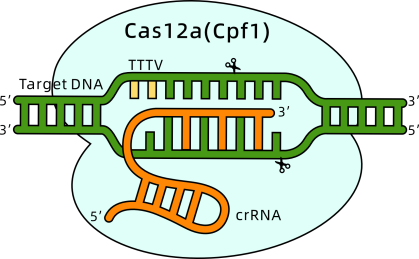
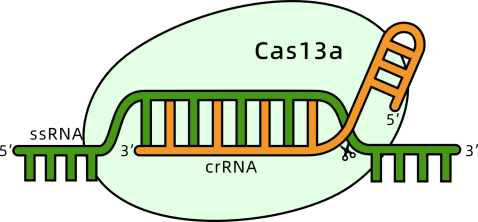
c) Other CRISPR Technologies
1. Article Title: Generation and characterization of a novel mouse model of Becker Muscular Dystrophy with a deletion of exons 52 to 55
Journal: Disease Models & Mechanisms (IF: 4.3)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.050595
A research team from Toronto has developed a novel mouse model for Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD) using CRISPR-Cas9. This new model features a deletion of exons 52 to 55, a mutation hotspot previously unreported in animal models of BMD.
The study compares various BMD models to better understand the function of different dystrophin isoforms and address the growing need for new therapeutic approaches for BMD.
2. Article Title: Engineered exosomes with a photoinducible protein delivery system enable CRISPR-Cas–based epigenome editing in Alzheimer's disease
Journal: Science Translational Medicine (IF: 15.8)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.adi4830
A research team from South Korea has developed a novel engineered exosome-based delivery system called MAPLEX. This system allows for the incorporation of cargo proteins fused with a photo-cleavable protein mMaple3 into exosomes, which are then targeted to specific exosome marker proteins.
The delivery system addresses the limitation of protein-based therapies being unable to cross cell membranes, which hinders the successful treatment of many diseases. The system was successfully used for targeted epigenome editing in the brains of two Alzheimer's disease models.
The study provides evidence that MAPLEX could be an effective intracellular protein delivery system, offering potential for treating a range of diseases through protein-based therapies.
II. Industry News
1. Fierce Biotech Announces 2024 Fierce 15
Fierce Biotech recently unveiled its 2024 Fierce 15 list, highlighting the 15 most promising and innovative biotech companies. This year's list includes several gene-editing companies, such as Ascidian Therapeutics, Excision BioTherapeutics, and iECURE.
https://www.fiercebiotech.com/special-reports/introducing-fierce-biotechs-2024-fierce-15
2. Sangamo Therapeutics and Genentech Licensing Agreement
Sangamo Therapeutics has entered into a licensing agreement with Genentech to develop genomic medicines for neurodegenerative diseases, focusing on Sangamo's zinc finger repressor targeting the tau gene associated with Alzheimer's disease and a second undisclosed target.
The agreement includes an exclusive license for Sangamo's STAC-BBB, a neurotropic AAV capsid with strong brain-penetrating abilities. Sangamo will receive $50 million upfront, with potential earnings of up to $1.9 billion, as it continues to explore further partnerships for its genomic technologies.
3. Beam Therapeutics Reports Pipeline Updates and Q2 2024 Financial Results
Beam Therapeutics has announced significant progress in its clinical programs using base editing technology, including successful patient recruitment and dosing in the BEACON trial for sickle cell disease. The company has also initiated trials for genetic diseases such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and glycogen storage disease type Ia.
4. 2seventy bio Q2 2024 Financial Results and Operational Updates
2seventy bio has released its Q2 2024 financial results, highlighting progress on ABECMA®, a CAR-T cell therapy for treating certain types of hematologic malignancies, particularly relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
5. CRISPR Therapeutics Q2 2024 Financial Results and Business Updates
CRISPR Therapeutics has provided updates on its Q2 2024 financial results and ongoing clinical trials, including progress on CASGEVY™, the first approved CRISPR-based gene therapy, and several other clinical trials currently underway.
EDITGENE focuses on CRISPR technology, offering a range of high-quality gene editing services and in vitro diagnostic products.
These include but are not limited to:CRISPR Library Screening, Cell Line Engineering, Monoclonal Cell Line Screening, and CRISPR Detection.
We are committed to providing the most efficient technical services for CRISPR-related, gene function research, in vitro diagnostics, and therapeutic research.
.
Recent Blogs:
1.[Literature Review] CRISPR KO Screening Reveals Key Genes Responsible for Chemotherapy Resistance
3.[Literature Review] CRISPR-Cas12a Exhibits Metal-Dependent Specificity Switching
Follow us on social media
Contact us
+ 833-226-3234 (USA Toll-free)
+1-224-345-1927 (USA)
info@editxor.com






